Iron Bisglycinate vs. Ferrous Sulfate: A Comprehensive Guide
Iron deficiency is a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. To combat this deficiency, various iron supplements are available, with iron bisglycinate and ferrous sulfate being two of the most popular options. In this article, we will compare iron bisglycinate and ferrous sulfate, discussing their benefits, absorption rates, and suitability for different individuals.
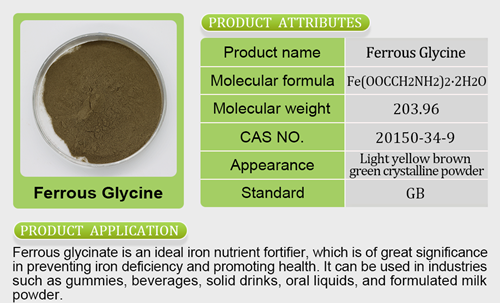
What is Iron Bisglycinate?
Iron bisglycinate is a chelated form of iron, meaning it is bonded to the amino acid glycine. This chelation enhances its absorption and bioavailability in the body, making it a popular choice among those who require iron supplementation. Iron bisglycinate is known for its gentle nature on the stomach, reducing the likelihood of gastrointestinal side effects often associated with other forms of iron.
Benefits of Iron Bisglycinate
1. Enhanced Absorption: The chelation process improves the absorption of iron in the intestinal tract, allowing for more efficient utilization by the body.
2. Reduced Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Many users report fewer digestive issues, such as constipation, nausea, and stomach cramps, compared to other iron supplements.
3. Higher Bioavailability: Iron bisglycinate is more bioavailable than other forms of iron, meaning that a larger percentage of the ingested iron is effectively used by the body.
What is Ferrous Sulfate?
Ferrous sulfate is one of the most commonly prescribed forms of iron supplements. It is a salt of iron that is often used to treat iron deficiency anemia. While it is effective in increasing iron levels, ferrous sulfate can cause some adverse gastrointestinal effects.
Benefits of Ferrous Sulfate
1. Widely Available: Ferrous sulfate is easily accessible and often recommended by healthcare professionals.
2. Cost-Effective: Generally, ferrous sulfate is less expensive than other iron supplements.
3. Effective for Iron Deficiency: It is a well-studied and proven option for treating iron deficiency anemia.
Iron Bisglycinate vs. Ferrous Sulfate: Key Differences
1. Absorption Rates
Iron bisglycinate has a higher absorption rate compared to ferrous sulfate. Studies suggest that the body can absorb iron bisglycinate more efficiently, leading to better results in increasing iron levels.
2. Gastrointestinal Tolerance
Individuals who have experienced gastrointestinal discomfort with ferrous sulfate often find iron bisglycinate to be a more tolerable option. The chelated form is less likely to cause constipation and other digestive issues.
3. Bioavailability
Iron bisglycinate’s bioavailability is superior, which means that a smaller dose can be as effective as a larger dose of ferrous sulfate. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who may have difficulty taking large pills or capsules.
Who Should Choose Which Supplement?
– Iron Bisglycinate: Ideal for individuals with sensitive stomachs, those who have experienced side effects from other iron supplements, or anyone looking for a highly absorbable form of iron.
– Ferrous Sulfate: Suitable for individuals seeking a cost-effective solution and those who do not have a history of gastrointestinal issues.
Conclusion
Choosing the right iron supplement can make a significant difference in managing iron deficiency. Iron bisglycinate offers superior absorption and fewer side effects, making it a preferred choice for many. On the other hand, ferrous sulfate remains a widely used and effective option. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement to determine the best option for your specific needs.
By understanding the differences between iron bisglycinate and ferrous sulfate, you can make an informed decision and take the necessary steps towards improving your iron levels and overall health.




