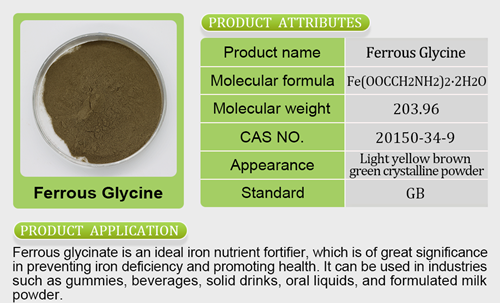
Chelated Zinc or Not: Understanding the Benefits and Drawbacks
When it comes to dietary supplements, zinc is often touted for its numerous health benefits, including immune support, wound healing, and its role in cellular metabolism. However, consumers frequently encounter the term “chelated zinc,” leading to the question: Should you choose chelated zinc or not? In this article, we’ll explore what chelated zinc is, its advantages and disadvantages, and ultimately help you make an informed decision about your zinc supplementation.
What is Chelated Zinc?
Chelated zinc refers to zinc that has been bound to an amino acid or another molecule, creating a complex. This process is designed to enhance the absorption of zinc in the body. Common forms of chelated zinc include zinc bisglycinate and zinc methionine. The chelation process can potentially improve the bioavailability of zinc, meaning your body can use it more effectively.
Benefits of Chelated Zinc
1. Improved Absorption: One of the primary advantages of chelated zinc is its enhanced absorption compared to non-chelated forms. Studies suggest that chelated minerals are better absorbed in the intestines, which can lead to higher serum zinc levels.
2. Reduced Gastrointestinal Distress: Some individuals experience stomach upset or nausea when taking standard zinc supplements. Chelated zinc is often better tolerated, making it a suitable option for those with sensitive stomachs.
3. Enhanced Bioavailability: The chelation process helps zinc to remain stable and bioavailable, which may lead to more effective supplementation and better health outcomes.
4. Potentially Fewer Side Effects: With improved absorption and reduced gastrointestinal issues, chelated zinc may present fewer side effects, making it a more appealing option for long-term supplementation.
Drawbacks of Chelated Zinc
1. Cost: Chelated zinc supplements are often more expensive than their non-chelated counterparts. For those on a budget, this could be a significant consideration.
2. Not Always Necessary: For individuals with a balanced diet rich in zinc, such as those consuming meat, shellfish, legumes, and seeds, chelated zinc may not be necessary. Regular dietary intake may provide sufficient levels of this essential mineral.
3. Variable Quality: Not all chelated zinc supplements are created equal. The quality of the chelation process can vary among manufacturers, leading to inconsistent absorption rates and effectiveness. It’s essential to choose reputable brands when considering supplementation.
When to Consider Chelated Zinc
If you’re considering zinc supplementation, chelated zinc may be a good choice under certain circumstances:
– Deficiency: If you have been diagnosed with a zinc deficiency or are at risk due to dietary restrictions, malabsorption issues, or certain health conditions, chelated zinc may help improve your levels more effectively.
– Immune Support: If you’re looking to bolster your immune system, especially during cold and flu season, chelated zinc can be a beneficial addition to your regimen.
– Gut Sensitivity: For those who experience digestive issues with standard zinc supplements, chelated forms may provide a gentler alternative.
Conclusion
In the debate of chelated zinc or not, the decision ultimately depends on your individual health needs, dietary habits, and budget. While chelated zinc offers enhanced absorption and reduced gastrointestinal discomfort, it may not be necessary for everyone. Always consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplements to your routine, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
By understanding the pros and cons of chelated zinc, you can make a more informed choice that supports your health and wellness goals. Whether you opt for chelated zinc or not, maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for overall well-being.




