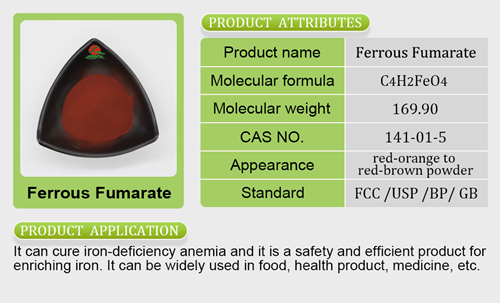
Zinc Bisglycinate vs. Zinc Citrate: Which Supplement is Right for You?
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including immune response, protein synthesis, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. When it comes to choosing a zinc supplement, two popular forms often come up: zinc bisglycinate and zinc citrate. But how do these two forms compare, and which one is the best option for you? In this article, we’ll explore the differences, benefits, and potential drawbacks of zinc bisglycinate and zinc citrate.
What is Zinc Bisglycinate?
Zinc bisglycinate is a chelated form of zinc that combines zinc with the amino acid glycine. This chelation process enhances the bioavailability of zinc, meaning that the body can absorb it more efficiently. Because it is bound to glycine, zinc bisglycinate is often gentler on the stomach compared to other forms of zinc, making it a preferred choice for those who experience gastrointestinal discomfort with supplements.
Benefits of Zinc Bisglycinate
1. High Bioavailability: The chelation with glycine improves absorption rates, ensuring that your body gets the maximum benefits from the zinc.
2. Gentle on the Stomach: This form is less likely to cause digestive issues, such as nausea or upset stomach, making it suitable for those with sensitive digestive systems.
3. Supports Immune Health: Zinc bisglycinate is known to enhance immune function, helping the body fight off infections more effectively.
What is Zinc Citrate?
Zinc citrate is another popular form of zinc supplementation. It consists of zinc combined with citric acid, which also aids in the absorption of zinc. While not as highly bioavailable as zinc bisglycinate, zinc citrate is still a well-absorbed form of the mineral.
Benefits of Zinc Citrate
1. Good Absorption: Zinc citrate has decent bioavailability and is generally well-absorbed by the body, making it an effective option for supplementation.
2. Taste: Zinc citrate often has a more palatable taste than other zinc supplements, which may make it more appealing for those who prefer flavored options.
3. Supports Overall Health: Like other forms of zinc, zinc citrate supports immune function, skin health, and cellular function.
Zinc Bisglycinate vs. Zinc Citrate: Key Differences
– Bioavailability: Zinc bisglycinate generally offers higher bioavailability compared to zinc citrate, meaning more zinc is absorbed into the bloodstream when taking zinc bisglycinate.
– Digestive Tolerance: Zinc bisglycinate is often better tolerated by those with sensitive stomachs, while zinc citrate may cause mild digestive discomfort in some individuals.
– Formulation: Zinc bisglycinate is chelated, which enhances its absorption, whereas zinc citrate relies on citric acid for absorption.
Which Supplement Should You Choose?
The choice between zinc bisglycinate and zinc citrate ultimately depends on your individual needs and preferences.
– If you have a sensitive stomach or have experienced digestive issues with other zinc forms, zinc bisglycinate may be the better choice for you due to its gentler nature.
– If you are looking for a well-absorbed zinc supplement that is easy to take and possibly more palatable, zinc citrate may suit your needs.
Conclusion
Both zinc bisglycinate and zinc citrate are effective forms of zinc supplementation, each with its own set of advantages. When choosing between the two, consider factors such as bioavailability, digestive tolerance, and personal preferences. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to determine the best option for your health needs. By making an informed choice, you can ensure that you are getting the most out of your zinc supplement and supporting your overall well-being.




